Cyber-attacks are increasing every day and are now considered as the third highest global risk, according to the World Economic Forum. GSMA’s mobile telecommunications security threat landscape report of 2019 says, “there was a 55% increase in breaches caused by open-source software vulnerabilities”.
Addressing security vulnerabilities is a top priority for DSPs because a successful cyber-attack could essentially cause disruption in service for millions of customers, loss of customers’ trust, deterioration of DSP’s brand & reputation and shutdown of operations.
Addressing security threats will require DSPs to establish a systematic process for vulnerability management with high levels of automation, to discover new vulnerabilities, perform a risk assessment and assign the vulnerabilities to the right support group to facilitate quicker remediation.
Depending on the DSP’s size, infrastructure and complexity and state of the configuration management database (CMDB), finding the responsible asset owner may prove to be a highly challenging and cumbersome task resulting in lead times of up to many weeks.
Vulnerability management process in DSPs network ecosystem involves scanning various subnets –telecom cloud, OSS/BSS, and telecom infra. Once the scanning is complete, a report will be generated with the list of vulnerable IPs and ports and the report is sent for risk analysis & vulnerability assignment. Vulnerability assignment involves assigning the vulnerabilities to the appropriate support group so that they can work on remediation. There might be different support groups such as device, application, database, and server support group.
Why is vulnerability assignment process so complex?
DSPs have an average of 400,000+ configuration items (CI’s) in their infrastructure and 80,000+ vulnerabilities getting identified in the scan (first-time scan) depending on their size of operations. All these vulnerabilities need to be assigned to the appropriate support group to work on remediation. By manual configuration management database (CMDB) administration & assignment, close to 70% of vulnerabilities are assigned to wrong support group and later rework to align them to the right group. Hence, the lead time significantly increases due to this bottleneck.
How to create and maintain a steady pipeline of high ROI opportunities for RPA implementation
The support groups manually administer all the attributes data and the required relationship between them for all the CIs. This generally leads to incompleteness in attributes data, inaccuracies in the mapping of the relationship between attributes and many times, data are simply not updated. Also, the inaccuracies in the mapping of the relationship between attributes exponentially increase the complexity, as one wrong mapping can lead to hundreds of vulnerabilities assigned to wrong support groups.
Proposed roadmap for seamless vulnerability analysis and assignment process
1. Introducing discovery scan that automatically scans, collects and updates the attributes data in CMDB
2. Introducing multi-vendor EMS system integration with CMDB that enables auto-updating of provisioning information
3. Building a central validation & CMDB data enrichment tool that aids in automated validation of attributes & relationships in CMDB
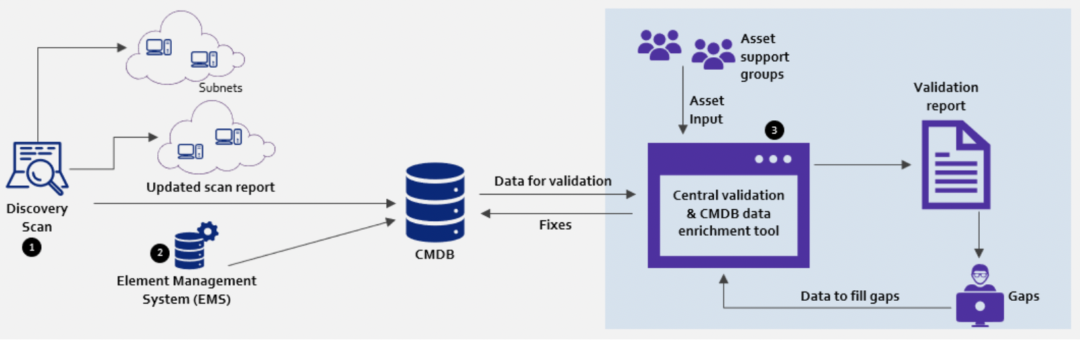
Discovery scan
- Discovery tooling needs to be deployed in the subnets and auto-run on a periodic basis, to fill the gaps or correct any incorrect information in CMDB
- Agent-based (such as Pressler PRTG) or agent-less (using SNMP, WMI, CIM protocols) discovery tooling can aid in keeping the CMDB up to date without requiring user interaction, and this helps in the quick discovery of attributes and their relationships (less than 15 minutes)
- Discovery tool keeps track of attributes which are relevant for the vulnerability management process such as IP addresses, subnets, OS, installed software, and the relationship between assets
Element Management Systems’ (EMS) integration with CMDB
- Multi-vendor element management systems need to be integrated with central CMDB & integration is established through ETL bus, which translates/reformats/enriches the data from EMS systems
- Reusable & customisable adaptors should be deployed to enable faster integration
- With this integration, any change (provisioning or decommissioning) of nodes will be automatically updated in the central CMDB
Central validation & CMDB data enrichment tool
Build a central validation & data enrichment tool that aids in finding gaps in CMDB databases. Further, the tool should also allow support groups to fix the gaps using the same tool.
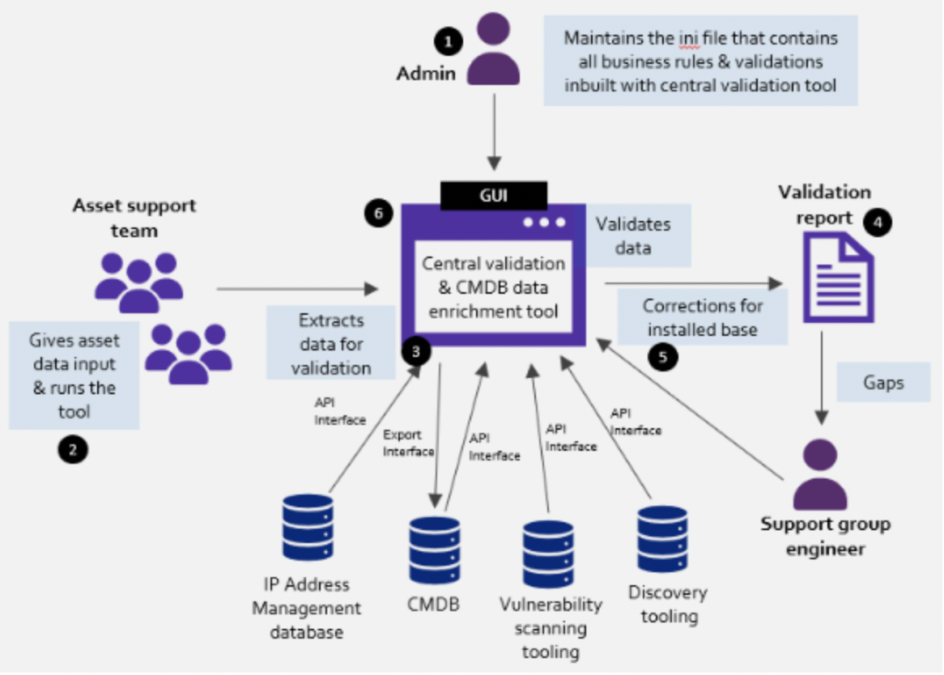
Central Validation & CMDB data enrichment tool workflow
- Admin creates/manages the customisable validation rule set
- Asset support team runs the central validation & CMDB data enrichment tool
- Central validation & CMDB data enrichment tool extracts the data from various databases and validates them on business rules
- Gaps are identified in all the databases, and the validation report gets published with the asset support group that is responsible for fixing the gaps
- Support group engineers from each asset support teamwork on fixing the gaps and send it to the respective databases through the central validation tool
- The validation happens after fixing gaps to ensure there are no more gaps in databases
Other key capabilities that need to be built on central validation & CMDB data enrichment tool
- Identifying gaps in vulnerability scanning and discovery scanning to improve coverage
- Identifying inaccuracies in the relationship between configuration items
- Identifying missing attributes such as IP addresses, network devices, servers, etc.
- Identifying inaccuracies in attributes relevant for vulnerability management (lifecycle status, DTAP pipeline, scanner zone, scan exclusions, etc.)
- Identifying inaccuracies in manual administration (e.g. support group data, missing IP subnets data, & incorrect interface port)
Benefits of using the proposed strategy
With a robust solution approach in place, DSPs can realise major benefits in the vulnerability management process such as:
- Time-saving: Improves vulnerability assignment time by 80% thereby improving the entire vulnerability management time by 50%
- Accuracy in data: CMDB administration complexity reduces, and accuracy of attributes and relationship data improves
- Enhanced security: Critical vulnerabilities that require immediate action could be remediated within the SLA
Written by Reza Nanoha, senior solution architect, Prodapt Consulting and Sathya Narayanan, assistant manager, strategic insights, Prodapt
Related articles
Gartner: debunking five artificial intelligence misconceptions
AI: A new route for cyber-attacks or a way to prevent them?
Enterprise AI adoption hampered by lack of skilled experts, says survey
Understanding the viability of blockchain in supply chain management
Driving business value with responsible AI
Emerging technologies, are they set to transform business?
UK tech sector leads Europe in AI — but what about the rest of the world?
EU artificial intelligence guidelines will help unlock potential of AI technology







