What a time to be alive! Is quantum computing no longer just a concept or theory?
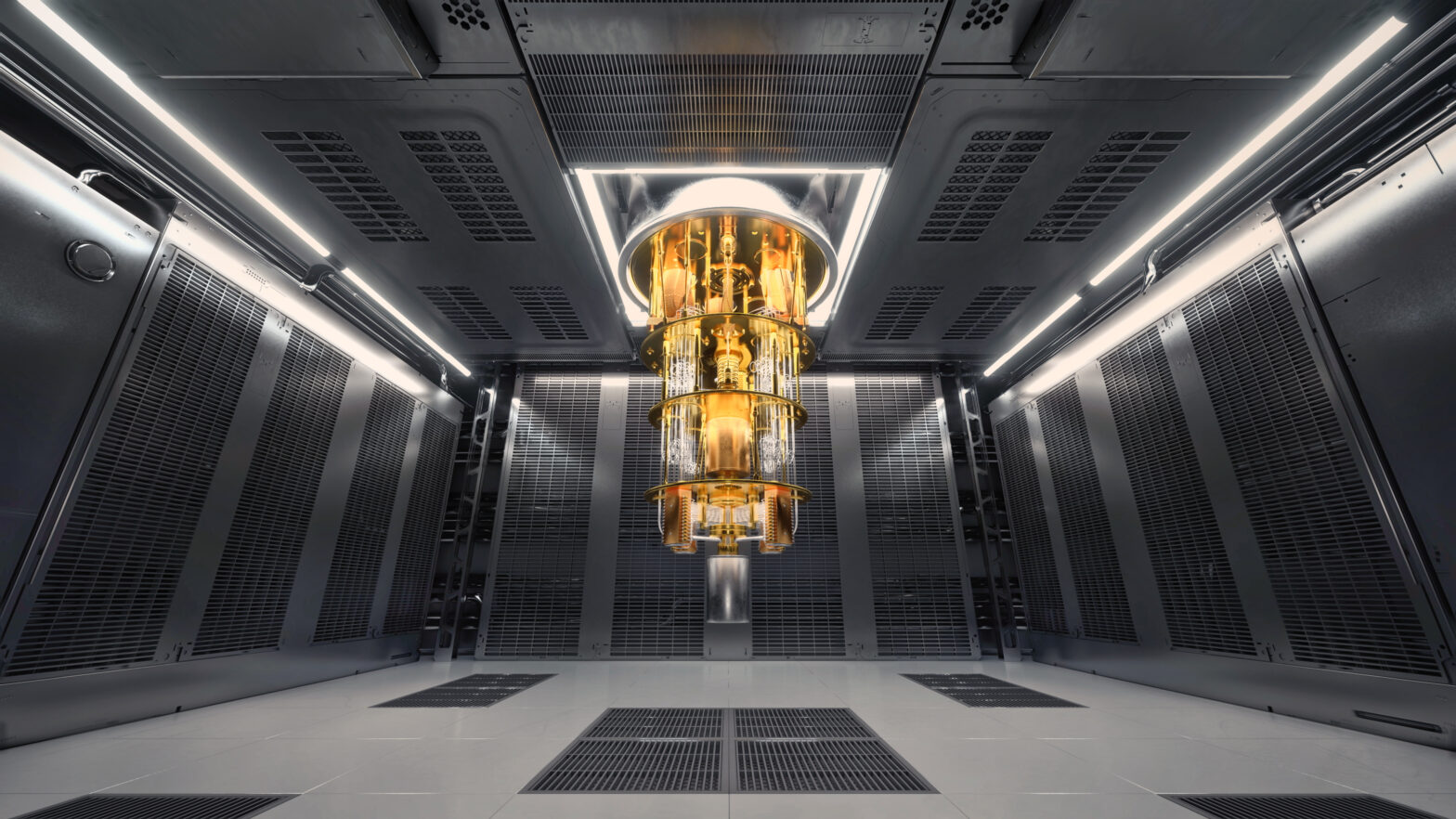
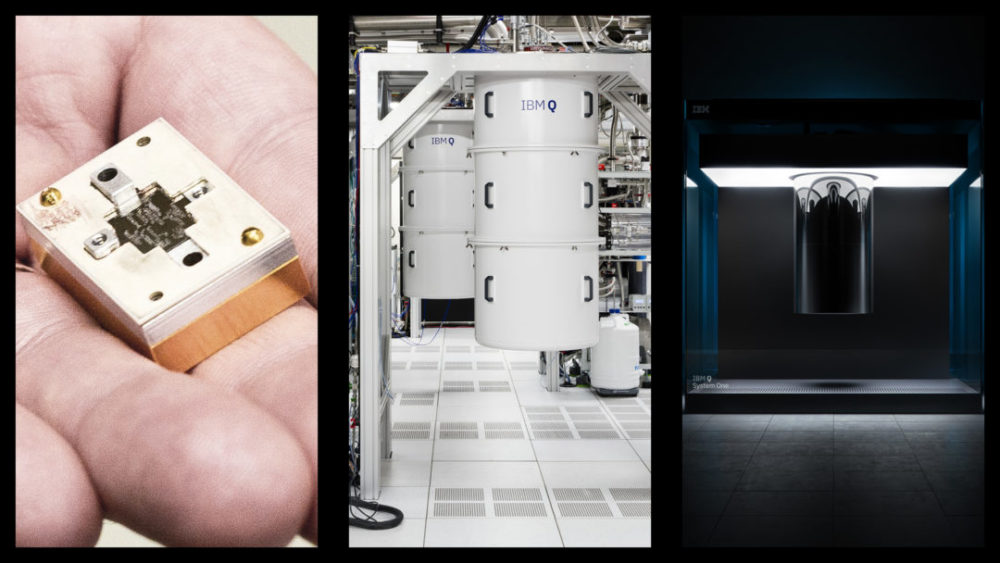
Back in 2017, IBM broke new ground when it announced it’s prototype commercial 17-qubit processor, forming the base for its IBM Q early-access systems. At the 2019 Consumer Electronics Show (CES), IBM took things even further, when it unveiled IBM Q System One — “the world’s first integrated universal approximate quantum computing system.”
“The IBM Q System One is a major step forward in the commercialisation of quantum computing,” said Arvind Krishna, senior vice president of Hybrid Cloud and director of IBM Research. “This new system is critical in expanding quantum computing beyond the walls of the research lab as we work to develop practical quantum applications for business and science.”
The top 10 strategic technology trends for 2019, according to Gartner
IBM Q systems are designed to one-day tackle problems that are currently seen as too complex and exponential in nature for classical computers to handle.
According to a spokesperson from the firm: “Future applications of quantum computing may include finding new ways to model financial data and isolating key global risk factors to make better investments, or finding the optimal path across global systems for ultra-efficient logistics and optimising fleet operations for deliveries.”
Designed by IBM scientists, systems engineers and industrial designers, IBM Q System One has a “sophisticated, modular and compact design optimised for stability, reliability and continuous commercial use.
RBC analysis of IBM Red Hat deal suggests boost to earnings will pay for acquisition cost
Q System One also boasts being the first “universal approximate superconducting quantum computers to operate beyond the confines of the research lab.”
IBM Q System One is composed of multiple custom segments that work together, including:
- Quantum hardware created to be enduring and auto-calibrated to provide repeatable and predictable high-quality qubits;
- Cryogenic engineering that delivers a constant cold and isolated quantum environment;
- High accuracy electronics in compact form factors to tightly control large numbers of qubits;
- Quantum firmware to manage the system health and enable system upgrades without downtime for users; and
- Classical computation to provide secure cloud access and hybrid execution of quantum algorithms.
The IBM Q Quantum Computation Center
IBM also announced plans to open its first IBM Q Quantum Computation Center for commercial clients in Poughkeepsie, New York in 2019.
This new centre will house some of the world’s most advanced cloud-based quantum computing systems, which will be accessible to members of the IBM Q Network, a worldwide community of leading Fortune 500 companies, startups, academic institutions, and national research labs working with IBM to advance quantum computing and explore practical applications for business and science.
Microsoft UK CTO provides his standout technology predictions