The rise in remote working and increased interest in health monitoring during the Covid-19 pandemic were cited as key factors in the forecasted growth of the wearable devices market over 2021.
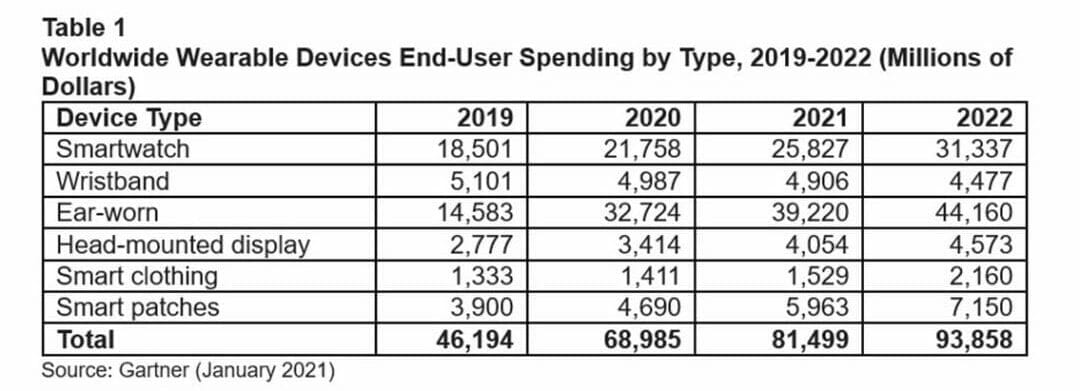
Spending on ear-worn devices rose by 124% to $32.7 billion in 2020, and and is forecast to reach $39.2 billion in 2021. Major factors in this growth, according to Gartner, can be earphone upgrades among remote workers for the purpose of video calls, and purchases being made with smartphones.
Smartwatch devices is also forecasted to see growth continue through 2021, driven in part by new users entering the market; end-user spending increased 17.6% to $21.8 billion in 2020, and Gartner predicts this figure to reach $25.8 billion this year, as improvements to battery life and charging times are made.
Smart watches, meanwhile, were added as a new category in the latest Gartner forecast, and are projected to reach almost $6 billion this year, up from $4.7 billion in 2020.
“The introduction of health measures to self-track Covid-19 symptoms, along with increasing interest from consumers in their personal health and wellness during global lockdowns, presented a significant opportunity for the wearables market,” said Ranjit Atwal, senior research director at Gartner.
“Ear-worn devices and smartwatches are seeing particularly robust growth as consumers rely on these devices for remote work, fitness activities, health tracking and more.
“Smart patches have been around for some time, but adoption has been slow due to strict regulatory compliance and resistance from both users and medical staff to adopt automated drug administration.
“The shift to e-health, especially during Covid-19, will transform users’ perceptions of automated health provision and increase the demand for smart patches.”
Sensor innovation and miniaturisation
Also driving growth in the wearable device space are improvements in sensor accuracy, which are causing the performance gap between medical- and nonmedical-grade wearables to close.
In addition, device manufacturers becoming able to integrate sensors into wearables that are nearly invisible to the end user, such as in the Oura Ring, Spire Health Tag or Proteus Discover, has also been an influencing factor. This process is known as miniaturisation.
Gartner predicts that by 2024, miniaturising capabilities will advance to the point that 10% of all wearable technologies will become unobtrusive to the user.
The importance of wearable hardware in the enterprise
“The capability of embedded sensors is often a determining factor in the reliability and usefulness of a wearable product,” said Atwal.
“Given the sensor improvement trend seen over the last several years, sensors built into wearable devices will be increasingly capable of more accurate readings, driving market growth over the next 3-5 years.
“Continued advances in miniaturisation and integration will enable further use cases and benefit adoption of smart garments, printed wearables, ingestibles and smart patches.
“These discrete and nearly invisible wearables will be particularly relevant and accepted by traditionally reluctant end-users, such as elderly patients who require medical applications but don’t want to call attention to the device or their ailment.”






