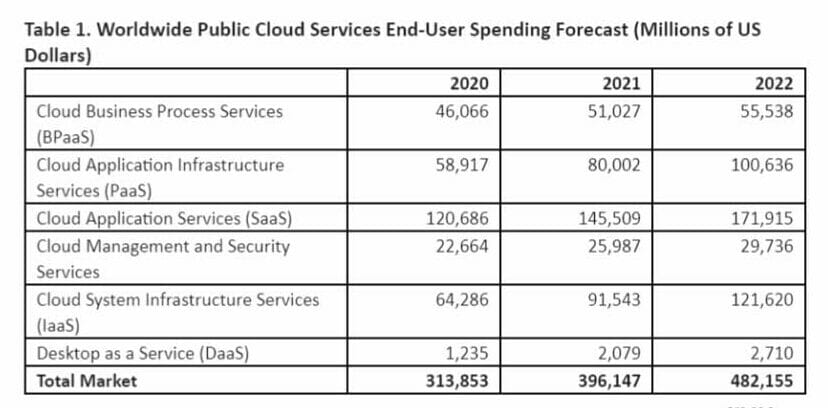
With global end-user spending on public cloud services expected to exceed $480 billion next year, the market trends revealed by Gartner are continuing to expand the breadth of cloud offerings and capabilities accelerating growth across all segments.
“The economic, organisational and societal impact of the pandemic will continue to serve as a catalyst for digital innovation and adoption of cloud services,” said Henrique Cecci, senior research director at Gartner.
“This is especially true for use cases such as collaboration, remote work and new digital services to support a hybrid workforce.”
These four public cloud trends are as follows:
Cloud ubiquity
With the cloud currently underpinning most new technological disruptions, including composable business, as well as providing resiliency, scalability, flexibility and speed to ease pandemic uncertainty, public cloud is set to be ubiquitous across businesses globally.
Hybrid, multi-cloud and edge environments are growing and setting the stage for new distributed cloud models, and new wireless communications advances such as 5G R16 and R17 will push cloud adoption to a new level of broader and deeper usage, according to Gartner.
The research company forecasts end-user spending on public cloud services to reach $396 billion in 2021, before growing by 21.7% to reach $482 billion in 2022, and exceed 45% of all enterprise IT spending by 2026.
Brandon Medford, senior principal analyst at Gartner, commented: “Organisations are advancing their timelines on digital business initiatives and moving rapidly to the cloud in an effort to modernise environments, improve system reliability, support hybrid work models and address other new realities compelled by the pandemic.”
Regional cloud ecosystems
Growing geopolitical regulatory fragmentation, protectionism and industry compliance are driving the creation of new regional and vertical cloud ecosystems and data services.
Companies in the financial and public sectors are looking to reduce critical lock-in and single points of failure with their cloud providers outside of their country.
Regions not able to create or sustain their own platform ecosystems will have no choice but to leverage the platforms created in other regions and resort to legislation and regulation to maintain some level of control and sovereignty.
Additionally, concerns among politicians, academia and tech providers in these regions are increasing, leading to initiatives such as GAIA-X in European countries.
Navigating data sovereignty through complexity
Sustainability and “carbon-intelligent” cloud
Nearly half of the respondents in the 2021 Gartner CEO Survey believe climate change mitigation will have a significant impact on their business.
In response, cloud providers are instituting more aggressive carbon-neutral corporate goals, which creates new challenges for infrastructure and operations (I&O) leaders.
“New sustainability requirements will be mandated over the next few years and the choice of cloud services providers may hinge on the provider’s ‘green’ initiatives,” said Cecci.
Cloud infrastructure and platform service (CIPS) providers’ automated programmable infrastructure
Finally, Gartner expects the broad adoption of fully managed and artificial intelligence (AI)-/machine-learning (ML)-enabled cloud services from hyperscale CIPS providers, which will rapidly eliminate the operational burden of traditional I&O roles in the public cloud.
“Infrastructure is becoming programmable, and its operation is subsequently becoming automated,” said Cecci.
“Modern IT infrastructure, whether deployed in the data centre or consumed in the public cloud, requires less manual intervention and routine administration than its legacy equivalents.”







