Chances are if you work in the manufacturing sector, you’ll have heard of industry 4.0. This so-called “fourth revolution” is set to significantly change how industries work and how we produce goods. Advances in technology and digital services are triggering this change, enabling increased productivity, more flexibility, and greater efficiencies within industry-related sectors. Although yet to see mainstream adoption, wearable technology in particular, promises to unlock a magnitude of opportunities for businesses looking to keep up with industry 4.0.
Augmented Reality is one technology which is playing a major part as industry 4.0 gathers force. This comes as no surprise when you consider that global spending for Augmented Reality workforce technology is at an all-time high and forecasted to reach $23 billion by 2025.
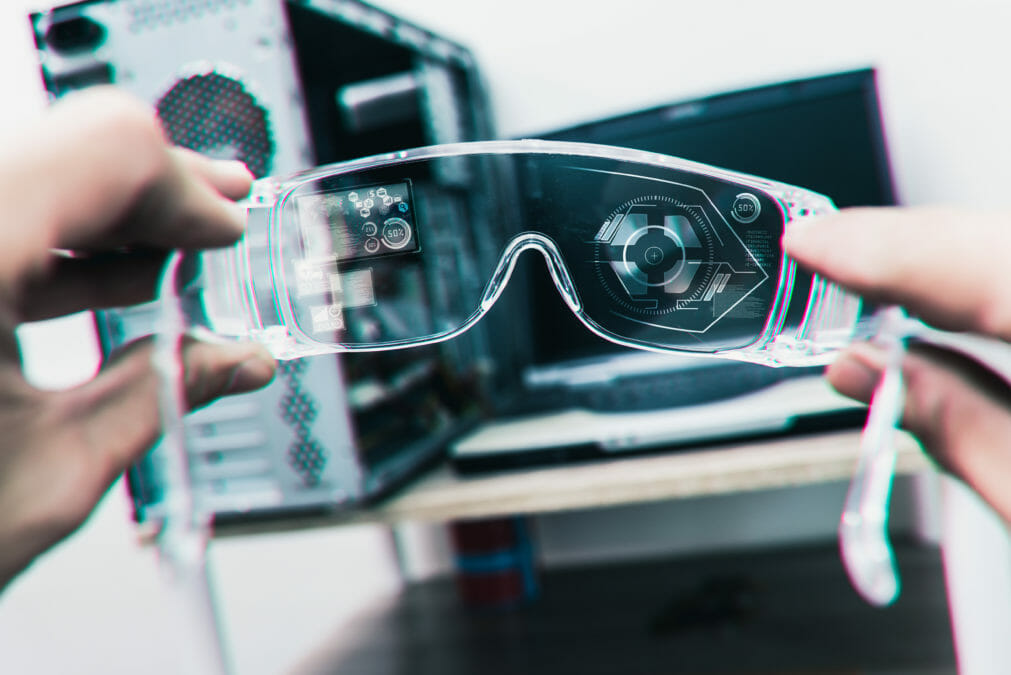
However, there is another technology which is predicted to drive industry 4.0 — assisted reality. This relatively new technology is having a particularly significant impact on industries with a heavy reliance on frontline and field-based workers, such as warehousing, manufacturing, healthcare, aerospace and automotive. So, what is assisted reality? How does it compare to its more well-known cousin augmented reality? And how exactly is it being used in industry?
Augmented reality: the new business tool driving industry 4.0
Assisted reality
Assisted reality refers to projecting additional information into a user’s field of vision, importantly hands-free. It differs from augmented reality in that it doesn’t change what the user is seeing, only adds an extra layer of information into their peripheral vision. Picture a heads-up display on a high-end car, projecting navigation instructions across the windscreen, and you’re on the right lines. To appreciate assisted reality’s accessibility and practicality for front-line workers within manufacturing and the technology’s transformative nature in relation to driving industry 4.0, it is important to discuss the potential assisted reality use cases across the entire company value chain.
For example, take a distribution or logistics warehouse where typically a high rate of picking takes place. Limiting “touches” can go a long way in improving efficiency. Vision picking capabilities on assisted reality smart glasses offer a faster, hands-free solution to help warehouse and other industrial employees work more effectively. Staff working in a warehouse setting can use “pick-by-vision” to improve efficiency of tasks from manual order picking, sorting, and inventory management stages, through to goods receipt and removal processes. Barcode scanning, having access to location assistance, and the use of voice conformations to run through checklists also enables next-level workflow optimisation for frontline workers.
Reshaping the professional landscape with digital transformation 2.0
Another example of how assisted reality can speed up production lines, improve workflows and reduce the number of errors is an automotive engineer using assisted reality smart glasses when building a car. Technicians can work on a vehicle and refer to checklists, other text or diagrams through a head-mounted viewer, keeping their hands-on tools at all time. If they run into difficulty, that can even use a video feed to show a more senior technician and get advice to complete a task. In the world of manufacturing time is money, and so too is quality. Getting the right support quickly increases effectiveness and efficiency of workforce, not only those on the front line but also remote workers who would otherwise need to be present at a job.
These examples are only some that demonstrate the potential that assisted reality can bring to businesses increasing their digital transformation efforts and embracing industry 4.0. The impact of this technology is specific to the sector, organisation and role, but it’s easy to see why assisted reality is so appealing. Providing a safe, efficient, hands-free and uninterrupted mobile working environment will continue to be a major catalyst for the uptake of assisted reality in the new industry 4.0 era.