Gartner has identified five distinct emerging technology trends that create and enable new experiences, leveraging artificial intelligence (AI) and other constructs to enable organisations to take advantage of emerging digital ecosystems.
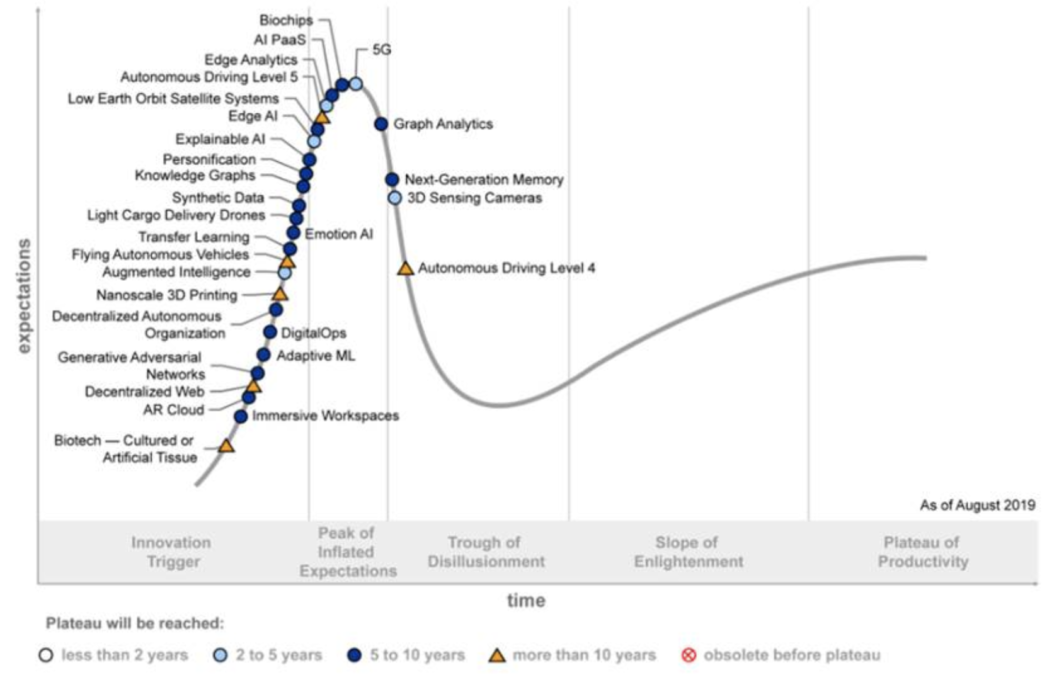
The five distinct emerging technology trends all featured on the 29 must-watch technologies on the Gartner Inc. Hype Cycle for Emerging Technologies, 2019, released today.
“Technology innovation has become the key to competitive differentiation. The pace of change in technology continues to accelerate as breakthrough technologies are continually challenging even the most innovative business and technology decision-makers to keep up,” said Brian Burke, research vice president at Gartner. “Technology innovation leaders should use the innovation profiles highlighted in the Hype Cycle to assess the potential business opportunities of emerging technologies.”
The five emerging technology trends
Sensing and mobility
According to Gartner, by combining sensor technologies with AI, machines are gaining a better understanding of the world around them, enabling mobility and manipulation of objects.
Sensing technologies are a core component of the Internet of Things (IoT) and the vast amounts of data collected. Utilising intelligence enables the ability to gain many types of insights that can be applied to many scenarios.
AI and IoT: two sides of the same coin
For example, over the next decade, Gartner said, AR cloud will create a 3D map of the world, enabling new interaction models and in turn new business models that will monetise physical space.
Organisations that are seeking leverage sensing and mobility capabilities should consider the following technologies: 3D-sensing cameras, AR cloud, light-cargo delivery drones, flying autonomous vehicles and autonomous driving Levels 4 and 5.
Augmented Human
Gartner said advances in technologies focused on augmenting people is enabling cognitive and physical improvements as an integral part of the human body. An example of this is the ability to provide superhuman capabilities such as the creation of limb prosthetics with characteristics that can exceed the highest natural human performance.
Emerging technologies focused on extending humans include biochips, personification, augmented intelligence, emotion AI, immersive workspaces and biotech (cultured or artificial tissue).
How augmented analytics tools will impact the enterprise
Postclassical compute and comms
Thanks to major improvements in traditional architectures — such as faster CPUs, denser memory and increasing throughput as predicted by Moore’s Law — classical core computing, communication and integration technologies have made significant advances. Gartner said this category includes not only entirely new approaches, but also incremental improvements that have potentially dramatic impacts.
For example, low earth orbit (LEO) satellites can provide low latency internet connectivity globally. These constellations of small satellites will enable connectivity for the 48% of homes that are currently not connected, providing new opportunities for economic growth for unserved countries and regions. “With only a few satellites launched, the technology is still in its infancy, but over the next few years it has the potential for a dramatic social and commercial impact,” said Burke.
Enterprises should evaluate technologies such as 5G, next-generation memory, LEO systems and nanoscale 3D printing.
Quantum computing — coming soon to an enterprise near you?
Digital ecosystems
Digital ecosystems leverage an interdependent group of actors (organisations, people and things) sharing digital platforms to achieve a mutually beneficial purpose. Digitalisation has facilitated the deconstruction of classical value chains, leading to stronger, more flexible and resilient webs of value delivery that are constantly morphing to create new improved products and services.
According to Gartner, the technologies to be considered for this category include DigitalOps, knowledge graphs, synthetic data, decentralised web and decentralised autonomous organisations.
Advanced AI & analytics
Advanced analytics comprises the autonomous or semiautonomous examination of data or content using sophisticated techniques and tools, typically beyond those of traditional business intelligence (BI).
“The adoption of edge AI is increasing for applications that are latency-sensitive (e.g., autonomous navigation), subject to network interruptions (e.g., remote monitoring, natural language processing [NLP], facial recognition) and/or are data-intensive (e.g., video analytics),” said Mr Burke.
The technologies to track include adaptive machine learning (ML), edge AI, edge analytics, explainable AI, AI platform as a service (PaaS), transfer learning, generative adversarial networks and graph analytics.
Related articles
Blockchain: a friend to digital continuity and lightweight workflow tool
Gartner releases first-ever Magic Quadrant for RPA software
Five AI advancements that are making intelligent automation more intelligent, by Sarah Burnett
Intelligent automation: Building the digital finance workforce of tomorrow
SaaS, Paas, XaaS, and more: looking behind the acronym